Debian Linux LVM配置手册(1)
Debian Linux LVM配置手册(1)
LVM - Logical Volume Manager 是Linux系统下最强大的磁盘管理技术之一.它将您从不得不思考物理容量中解脱出来,代之以逻辑形式来思考这些容量. 当您需要考虑如何替用户数据和系统文件分配空间的时候,LVM可以让您彻底忘记传统的分区做法.
简单地来说,LVM就是将众多物理设备组合成一个大的虚拟设备,用户只需思考如何在虚拟设备上做传统的空间分配策略,而将物理设备的管理交由LVM自己去处理.这个由物理设备组合所成的虚拟设备称为卷组(Volume Group),简称为VG;而用户在卷组VG上所划分的磁盘空间则称为逻辑卷(Logical Volume),简称为LV;而原始物理设备必须经过初始化处理才能加入卷组集合,这种经过特别处理的原始设备或磁盘空间则称为物理卷(Physical Volume),简称为PV.
LVM磁盘空间管理系统允许您在需要的时候重新调整大小, 这也就意味着在管理磁盘空间资源方面, 您将获得极大程度的自由. 基本上这是很有诱惑力的, 但您应该留心硬盘出错的情况,如果您没有在LVM管理中为出现这种情况而做好计划,那么您可能会丢失大量数据.
LVM 术语:
PV - Physical Volume 物理卷,例如一个硬盘,或一个Software RAID设备;
VG - Volume Group 卷组,将一组物理卷收集为一个管理单元;
LV - Logical Volume 逻辑卷,等同于传统分区,可看作便准的块设备,以容纳文件系统;
PE - Physical Extent 物理块,划分物理卷的数据块;
LE - Logical Extent 逻辑块,划分逻辑卷的数据块;
LVM 结构:
为了让大家了解关于LVM的概念和结构.实现方式等.作者花了整整一天时间画了一个图.
突然发现自己的”设计”水准很前卫很潮流. (谁说图片不好看谁就不要看文章了! :-))
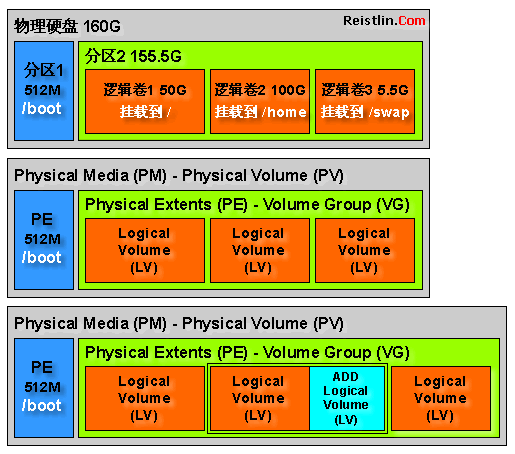
说明: /boot 这个挂载分区不能存在于VG卷组里.所以我们一般是建议单独分区.
使用LVM的基本步骤如下:
1. 安装lvm2 (apt-get install lvm2)
2. 使用fdisk分区指定的物理硬盘
3. 使用lvm管理工具进行lvm配置 (建立PV / VG / LV)
4. 格式化已经设置好的LV逻辑卷.挂载到指定目录.
5. 关于如何增加/删除/修改LV逻辑卷大小.请期待第2季.
LVM 配置步骤:
// 查看物理磁盘状态 - 硬盘(容量1GB) /dev/sdb 已经识别
Debian:/home/reistlin#fdisk -l
Disk /dev/sda: 10.7 GB, 10737418240 bytes
255 heads, 63 sectors/track, 1305 cylinders
Units = cylinders of 16065 * 512 = 8225280 bytes
Disk identifier: 0×0002db3a
Device Boot Start End Blocks Id System
/dev/sda1 1 1033 8297541 83 Linux
/dev/sda2 1034 1305 2184840 82 Linux swap / Solaris
Disk /dev/sdb: 1073 MB, 1073741824 bytes
128 heads, 32 sectors/track, 512 cylinders
Units = cylinders of 4096 * 512 = 2097152 bytes
Disk identifier: 0×00000000
Disk /dev/sdb doesn’t contain a valid partition table
// 使用 fdisk 对 /dev/sdb 分区
Debian:/home/reistlin#fdisk /dev/sdb
Device contains neither a valid DOS partition table, nor Sun, SGI or OSF disklabel
Building a new DOS disklabel with disk identifier 0×4e896764.
Changes will remain in memory only, until you decide to write them.
After that, of course, the previous content won’t be recoverable.
Warning: invalid flag 0×0000 of partition table 4 will be corrected by w(rite)
Command (m for help):new
Command action
e extended
p primary partition (1-4)
p
Partition number (1-4):1
First cylinder (1-512, default1):
Using default value 1
Last cylinder or +size or +sizeM or +sizeK (1-512, default512):
Using default value 512
Command (m for help): m
Command action
a toggle a bootable flag
b edit bsd disklabel
c toggle the dos compatibility flag
d delete a partition
l list known partition types
m print this menu
n add a new partition
o create a new empty DOS partition table
p print the partition table
q quit without saving changes
s create a new empty Sun disklabel
t change a partition’s system id
u change display/entry units
v verify the partition table
w write table to disk and exit
x extra functionality (experts only)
Command (m for help):w
The partition table has been altered!
Calling ioctl() to re-read partition table.
Syncing disks.
// 查看分区后的物理磁盘信息 - /dev/sdb1 状态正常
Debian:/home/reistlin#fdisk -l
Disk /dev/sda: 10.7 GB, 10737418240 bytes
255 heads, 63 sectors/track, 1305 cylinders
Units = cylinders of 16065 * 512 = 8225280 bytes
Disk identifier: 0×0002db3a
Device Boot Start End Blocks Id System
/dev/sda1 1 1033 8297541 83 Linux
/dev/sda2 1034 1305 2184840 82 Linux swap / Solaris
Disk /dev/sdb: 1073 MB, 1073741824 bytes
128 heads, 32 sectors/track, 512 cylinders
Units = cylinders of 4096 * 512 = 2097152 bytes
Disk identifier: 0×4e896764
Device Boot Start End Blocks Id System
/dev/sdb1 1 512 1048560 83 Linux
评论暂时关闭